Contents
What is a Microgrid?
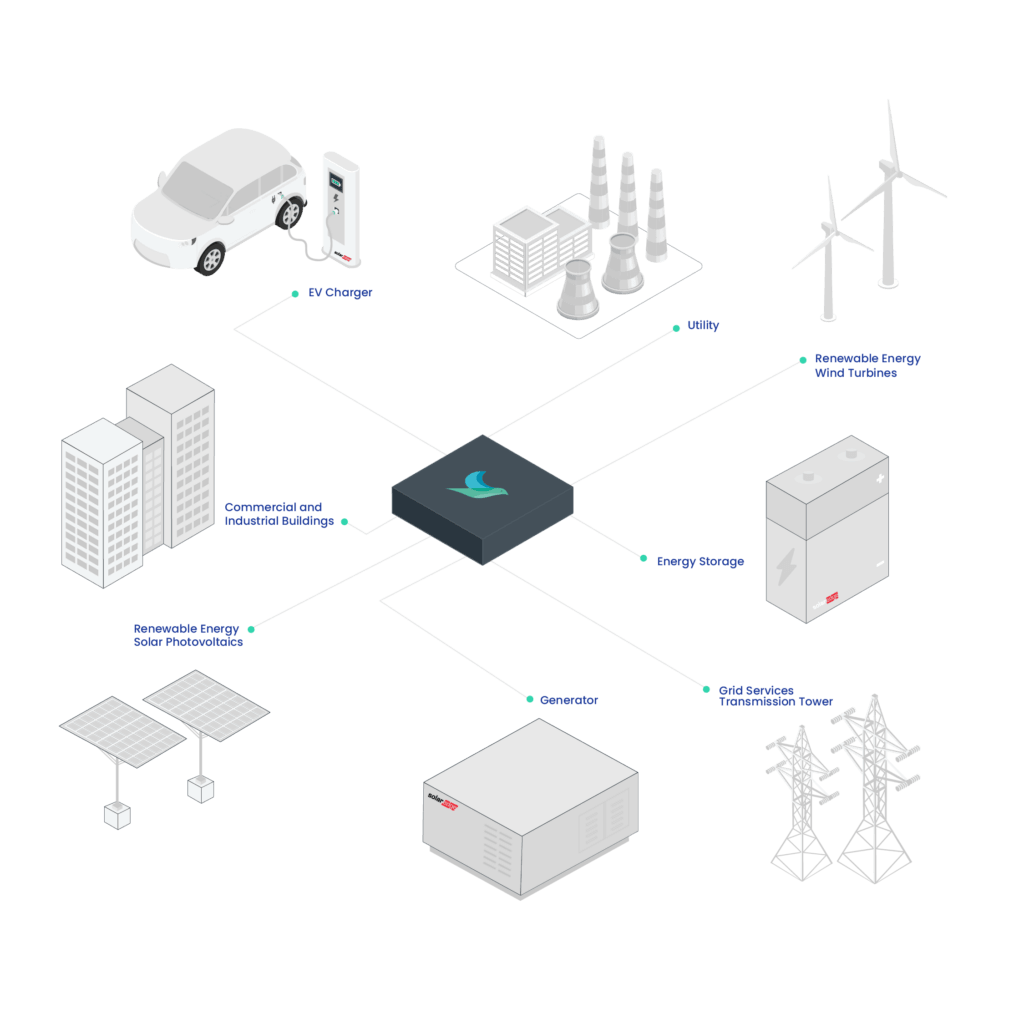
Microgrids are ‘small-scale power networks ’ that allow you to generate your own on-site electricity via different distributed energy sources such as Solar PV, Wind Turbines, Combined Heat and Power, Gas, Diesel Generators, Fuel Cells and so on. To be fully self-sufficient, Microgrids will often use Battery Energy Storage Systems to efficiently store energy and dispatch when generation is low.
Microgrids can provide power to remote locations without access to the national grid, or operate in conjunction with existing power networks to provide a supplemental, environmentally friendly supply of power to industrial complexes or local communities.
When used efficiently, this promotes self-consumption and greatly reduces wasted energy, while capitalising on renewables when they are in abundance (high sun, high wind, etc.). A major benefit of integrating a microgrid into your commercial or industrial estate is the ability to opt into grid services and therefore create an additional revenue stream whilst simultaneously saving on energy costs.
What are the Different Types of Microgrids?
There are 3 main types of microgrids:
Grid Connected
This kind of microgrid still has a physical connection to the main/national grid, which reduces pressure for on-site energy sources, such as Solar PV or Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS), to generate and store energy. Grid connected microgrids can also supply power back to the main grid, and therefore can still opt-into demand response/grid services.
Islanded Mode
Islanded mode is an operating condition where the microgrid is disconnected from the main power grid either intentionally or unintentionally due to a fault or outage with the national grid. These microgrids have the ability to operate by themselves to maintain power and are fully self-consuming. Isolated microgrids can be re-connected back to the main grid at any time.
Stand Alone (Isolated) Mode
This is a localised electrical grid that is completely isolated and cannot be connected to the main power grid. These types of Microgrids have their own sources of electricity and energy storage systems. These are commonly used where power transmissions and distribution distance from the main grid are too far and costly to put in place.
![]() A combination of renewable energy generation, energy storage and energy management software is vital for an efficient microgrid.
A combination of renewable energy generation, energy storage and energy management software is vital for an efficient microgrid.
What are the advantages of a Microgrid?
Improved electric reliability
Traditional power grids are susceptible to blackouts and other disruptions, microgrids are designed to operate independently to provide energy to the local communities/facilities in the event of any disruptions caused to the wider power grid. Microgrids can be configured to use redundant energy sources and distribution systems.
Enhanced resilience / recovery
In an event where there is an outage to the main power grid, for example, caused by a natural disaster or major power cut, a microgrid can provide backup power to critical infrastructure within a community including hospitals, police stations, fire stations, water treatment plants, etc. Microgrids are designed to be integrated with energy storage systems to store excess energy generated by the microgrid during periods of low demand which can then be used during periods when there is a high demand for energy.
Lowered energy costs for consumers and businesses
Using Microgrids reduces costs as they use methods to efficiently manage energy supply and maximise renewable energy that is generated on site. Microgrids supply revenue by selling energy and services back to the grid providing consumers with more control in the energy market.
Improved environment and promotes clean energy
Businesses and communities are striving to having cleaner energy goals and want to be able to conserve energy and reduce their impact on the environment through how much power they generate. Microgrids can help businesses and communities to do this as they have the capability to use a wide range of eco-friendly methods of energy production including solar, wind and combined heat and power plants.
Strengthened Central Grid
Microgrids don’t just serve their own customers, but they also benefit wider communities when used to strengthen the wider electric grid. This is done by helping to ease the strain on the central power grid during peak periods by acting as an additional resource during these periods.
Microgrids bring economic value to society
Power outages are extremely costly especially to businesses such as research facilities, data centres, manufacturers and retail. During a power outage to the central grid, Microgrids can act as a backup option averting loss and operation of businesses to the community. Through using an islanded approach from the main grid, there is a continuous supply to customers via on site generators averting significant economic loss meaning that workers can continue with their jobs as normal
Frequently Asked Questions
There are many complex nuances to microgrids and questions that may arise. Below are some of the most frequently asked questions:
Is Solar PV a microgrid?
Yes, Solar PV is a type of microgrid. Microgrids can distribute all kinds of energy resources including renewable energy or fossil fuels. Solar Microgrids are a specific type of microgrid that generates electricity using solar power. A commercial (or residential) solar panel system complete with battery storage is a type of solar microgrid.
What is the market size of microgrid control system?
The Microgrid Market size is expected to reach $13.37 billion in 2023 and grow at a CAGR of 19.08% to reach USD 32.01 billion by 2028.
What is a microgrid control system?
It is a centralised control device of the Microgrid that regulates output of the PV system, output and auxiliary ES’s and connection and disconnection of loads to maintain maximum PV output and continuous power supply to important loads, prevent overcharge and over discharge of batteries.
What is the difference between mini-grid and microgrid?
Microgrids are used by small residential or commercial consumers where Mini grids typically can power large commercial outlets, universities, factories and even islands. They can both complement the conventional power grid when electricity demand is high.
What is the capacity of a solar microgrid?
Microgrids commonly range in size from 100 kW to multiple MW.
To learn more and understand how our solution can fit into your system. Please get in touch with our tea
If you have any suggestions for improvements please tell us – Contact Us
